If you’re new to the Ubuntu Linux operating system, it’s natural to have questions about updating and upgrading the system as well as third-party software packages. Updating and upgrading are routine tasks that are commonly performed to maintain a system’s health and functionality.
In this article, we will see simple Ubuntu update packages commands to be used in the terminal. Commands will be explained in required detail, so you will use them at full potential.
Jump to,
What are packages and why update them?
Packages are bundles of software that contain programs, libraries, and other resources needed in archived format to run specific applications or perform certain tasks in the Linux operating system and so in Ubuntu. They are essential in Ubuntu because they simplify the process of installing, updating, and managing software.
Keeping your Ubuntu system updated is crucial to ensure its security and performance. Regularly updating all packages ensures that you have the latest,
- bug fixes
- security patches and
- exciting new features.
Ubuntu is a Linux-based operating system, that relies on a package management system to handle software installation, updates, and removal. The package manager, known as Advanced Package Tool (APT), is a powerful command-line tool that simplifies the process of managing software packages.
And, doing this is very simple and just two-three clicks task or easy as entering two commands in the terminal. But, first-time users always need a clear and informative guide.
Steps to Update All Packages on Ubuntu
There are multiple methods to update app packages in Ubuntu, here we will see steps to check and update all available software packages in Ubuntu at once using terminal apt commands.
Step 1: Open the terminal window
To begin, open the Terminal. You can do this by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T or by searching for “Terminal” in the application launcher. The Terminal is where you’ll enter commands to update your packages.
Step 2: Fetch the updated package list
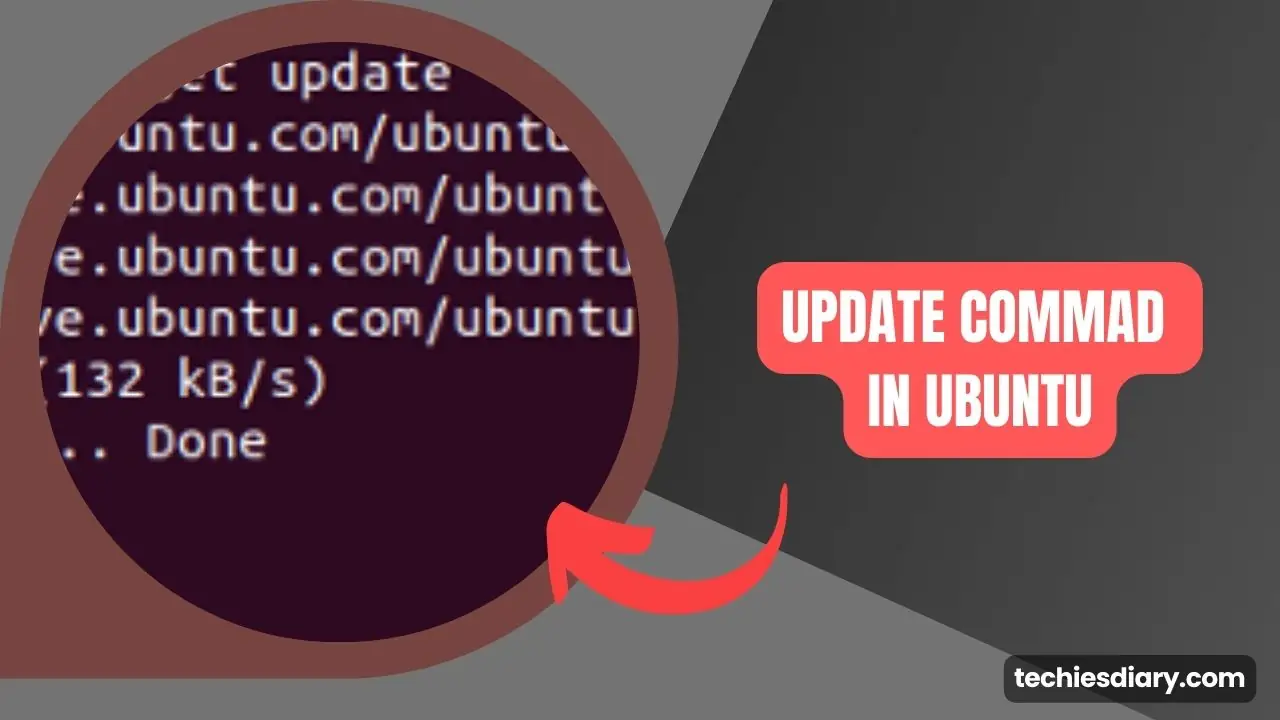
Before we update the packages, we need to make sure we have the latest information about available updates. It is just like we do “check updates” in another operating system. To do this, enter the following command in the Terminal:
sudo apt update
When you hit Enter after the previous command, Ubuntu will prompt you to enter your password. Don’t worry if you don’t see any characters appearing on the screen while typing—it’s a security measure. Type your password and press Enter.
Step 3: Check the upgradable package list
After updating the package lists, let’s see which packages have updates available. Type the following command:
sudo apt list --upgradable
This will display a list of packages that have updates waiting to be installed.
Step 4: Execute upgrade packages command
Now comes the exciting part—updating all the packages to their latest versions! Execute the following command:
sudo apt upgrade
Ubuntu will provide you with a summary of the packages that will be upgraded. It will also ask for your confirmation. To proceed with the upgrade, simply type “Y” and press Enter.
Note: During the upgrade process you may be asked to restart certain services. Just follow the on-screen instructions as needed.
Step 5: Cleaning Up leftover garbage
After the upgrade is complete, it’s a good idea to tidy up any leftover files that are no longer needed. Run the following command:
sudo apt autoremove
This command will remove any unnecessary packages and their associated dependencies, freeing up disk space on your system.
Step 6: Reboot the system if necessary
In some cases, a system reboot might be required for all the updates to take effect. If you receive such a notification, it’s recommended to restart your Ubuntu system. Don’t worry, Ubuntu will let you know if a reboot is needed.
More Info on the Ubuntu Package Update
It’s generally a good idea to update your packages regularly. Aim for at least once a week to ensure you have the latest security patches and software improvements.
Entering your password is necessary for making system-level changes. This is to ensure that only authorized users can modify critical system components.
Updating packages should not impact your personal files and settings. It primarily updates the software components and libraries on which your system relies.
If you don’t see any errors or upgradable packages, it means your system is already up to date. Remember that some updates might not be available immediately or specific to certain software repositories.
Setting Up Auto-Update
Ubuntu provides a convenient way to automate package updates. You can configure the system to automatically install security updates or even all updates.

To enable automatic updates, open the Software & Updates application (search “software update” in show applications available at the left bottom corner), navigate to the “Updates” tab, and select the desired options under the “Automatic updates” section.
Happy computing!????????
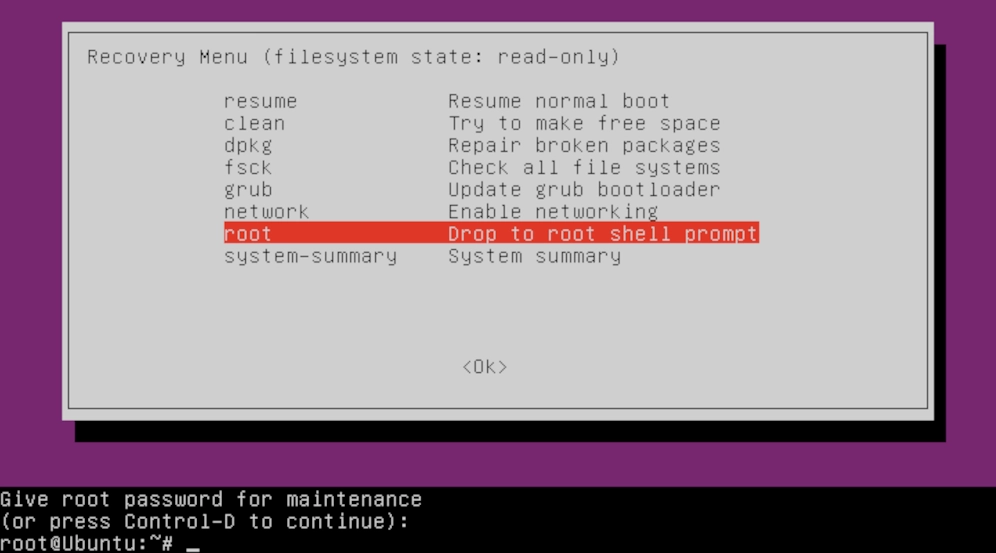

There are some errors that appear when first time user try to use sudo command, especially when running Ubuntu operating system in virtual box environment.